Display average and median for DORA4 metrics graphs
In this release, we’ve added the ability to view average deployment frequency rates and median lead times in your DORA4 metrics. You can now continuously monitor your DevOps process and quickly identify how you are actually performing versus your average or median pace.
Improved cleanup of gitconfig file
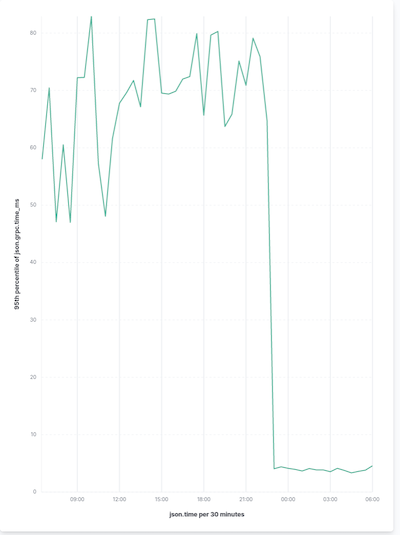
Gitaly parses .gitconfig files that can grow very large when not maintained. Large .gitconfig files can heavily impact the performance of short-running Git commands. GitLab 14.8:
- Resolves a known issue where we were not correctly cleaning up certain configuration keys as expected.
- Proactively removes empty configuration sections.
Combined, these updates improved performance by 50% or more for these short-running Git commands, resulting in a substantial reduction during regular Git operations!
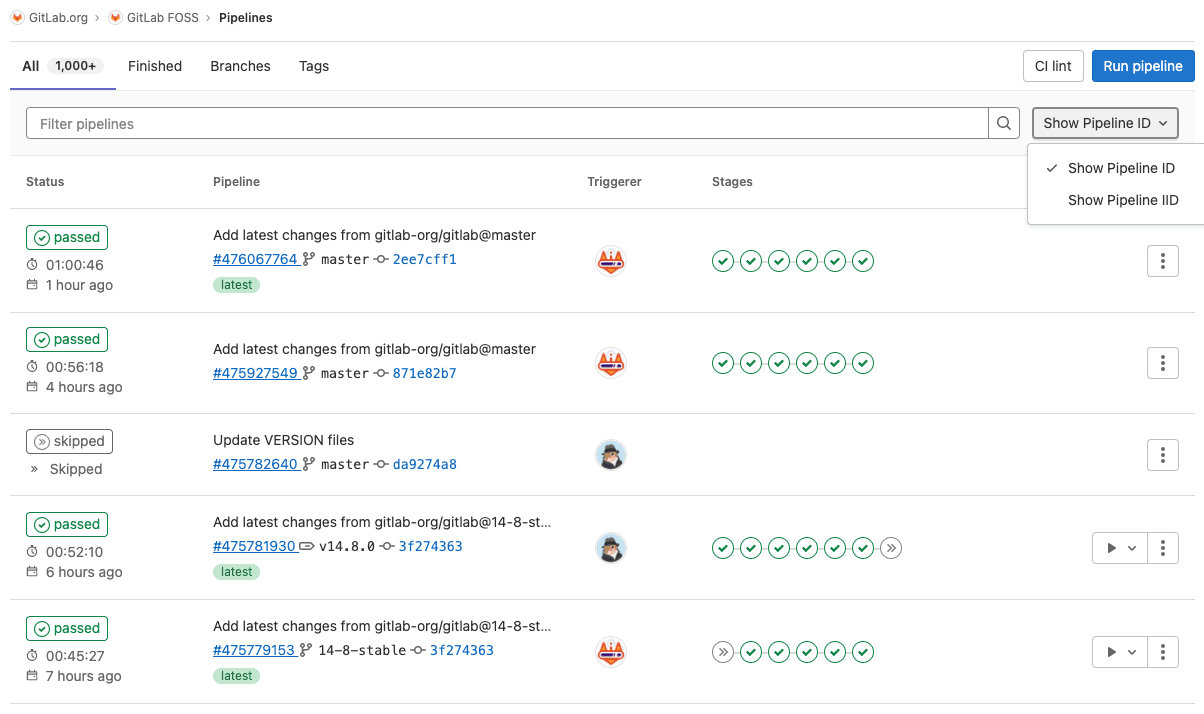
Improve pipeline index page layout
GitLab values efficiency, so we want to empower you to easily navigate our platform, especially when viewing jobs and pipelines. You might have noticed that the many options and columns on the job and pipeline index pages make it difficult to understand what GitLab CI/CD information is most relevant to your project.
Now, we have restructured these views so you can quickly get the pipeline information you need, including status, name of pipeline, merge request ID, and commit SHA.
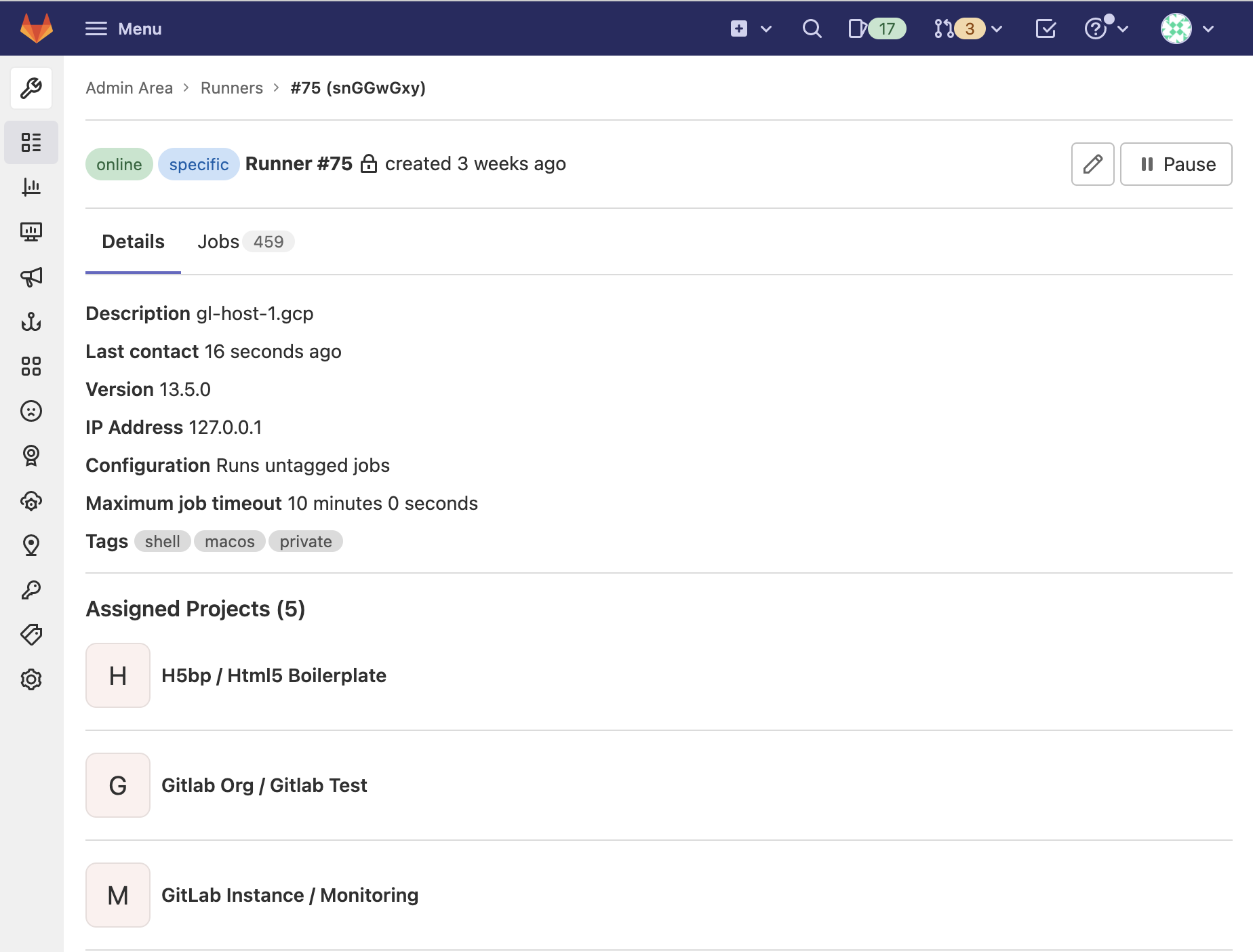
View read-only runner details in the Admin Area
You can now view the details of a runner in the Admin Area. This new view aims to provide the most valuable information about each runner associated with your GitLab instance. You can view last contact, runner version, and assigned projects, which is now paginated. In the new paginated jobs tab, you can also view a full list of jobs run by the Runner, which helps you view, search, and analyze CI/CD job execution history quickly.
The agent server for Kubernetes is enabled by default
The first step for using the agent for Kubernetes in self-managed instances is to enable the agent server, a backend service for the agent for Kubernetes. In GitLab 14.7 and earlier, we required a GitLab administrator to enable the agent server manually. As the feature matured in the past months, we are making the agent server enabled by default to simplify setup for GitLab administrators. Besides being enabled by default, the agent server accepts various configuration options to customize it according to your needs.
Customize built-in SAST and Secret Detection rules
You can now customize the predefined rules that are included in GitLab Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Secret Detection. For each rule, you can change the name, message, description, and severity fields to help your DevSecOps teams know which vulnerabilities to fix first.
This is an addition to the existing customization options in GitLab Ultimate, which allowed you to disable, replace, or extend predefined rules.
Your customizations are reflected in the gl-sast-report.json and gl-secret-detection-report.json artifacts, used when evaluating merge request approval rules, and shown in the Vulnerability Report.
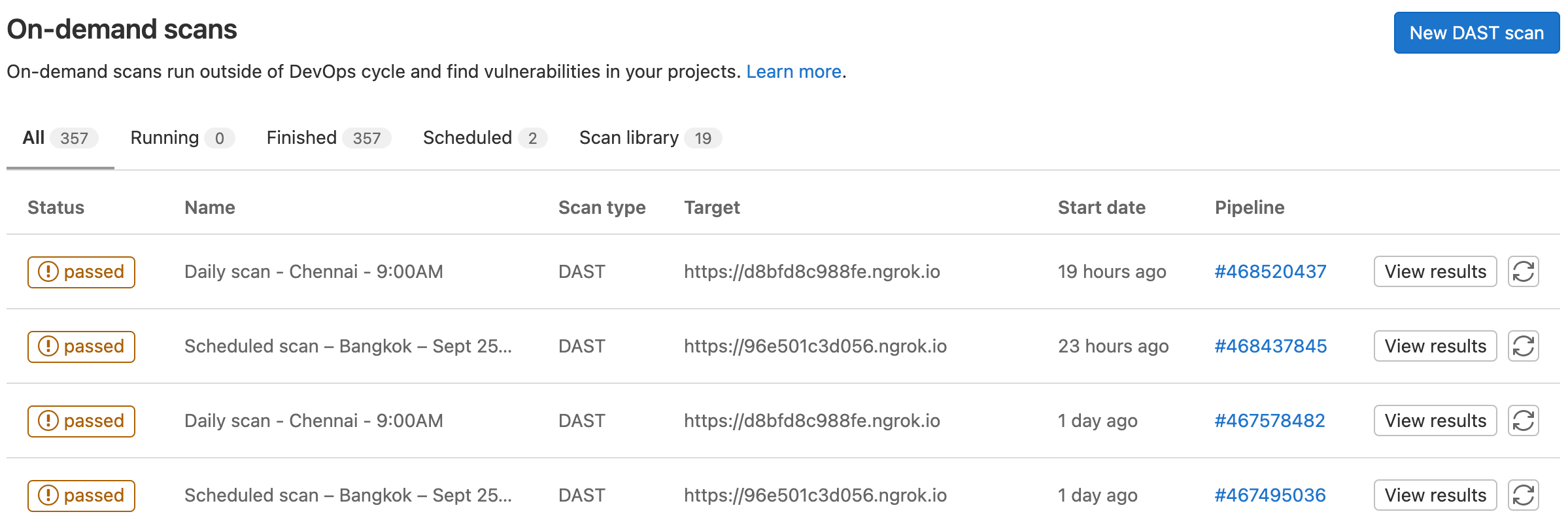
On-demand security scan index view
Find all your on-demand DAST and DAST API scans on a single page. We have introduced a new index page for on-demand scans that shows your in-progress scans, previously run scans, saved scans, and scheduled scans. From this index page, you can find specific scans easily or re-run scans that have already finished. In previous versions of GitLab, to see on-demand scans that were in-progress or had finished, you needed to search through the pipelines page to find the right pipeline. Saved on-demand scans were located in the Security & Compliance configuration section. To find scheduled scans, you needed to look at each saved scan individually to see their schedule. All of those activities are now rolled into one page to make it easier to run on-demand security testing outside of CI/CD builds, MRs, or pipelines.
Static Analysis analyzer updates
GitLab Static Analysis includes many security analyzers that the GitLab Static Analysis team actively manages, maintains, and updates. The following analyzer updates were published during the 14.8 release. These updates bring additional coverage, bug fixes, and improvements.
- Bandit analyzer updated to version 1.7.2. See CHANGELOG for details.
- New rules for SNMP configuration
- Resolved CVEs in Alpine Linux
- ESLint analyzer updated to version 6.2.0 of
eslint-plugin-html and version 7.28.0 of eslint-plugin-react. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Add, fix, and update various rules
- MobSF analyzer updated to version 3.4.6. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Reduce severity of some existing rules
- Add new rules for Android encryption settings and API calls
- Gosec analyzer updated to version 2.9.6. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Fix false negatives in some cases
- Semgrep analyzer updated to version 0.82.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Improve performance
- Add symbolic propagation for simple definitions,
x = foo.bar(); x.baz() matching foo.bar().baz()
- Fix various bugs
- Kics analyzer updated to version 1.5.1. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Add and update rules, fix various issues
- Disable network requests to send crash reports and fetch modified rule descriptions
- Kubesec analyzer updated to version 2.11.4. See CHANGELOG for details.
- NodeJS-scan analyzer updated to version 0.3.1. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Upgrade dependencies
- Fix and update rules
- Secrets analyzer updated to fix various issues and rules. See CHANGELOG for details.
- PMD Apex analyzer updated to version 6.42.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- SpotBugs analyzer dependencies updated. See CHANGELOG for details.
We’ve also updated the Go version used in the analyzers to address recent security issues in Go.
If you include the GitLab-managed SAST template (SAST.gitlab-ci.yml), you don’t need to do anything to receive these updates. However, if you override or customize your own CI/CD template, you need to update your CI/CD configurations. To remain on a specific version of any analyzer, you can pin to a minor version of an analyzer. Pinning to a previous version prevents you from receiving automatic analyzer updates and requires you to manually bump your analyzer version in your CI/CD template.
GitLab chart improvements
- GitLab 14.8 includes an update of the Prometheus Helm chart from
11.16.9 to 15.0.4, which brings us from Prometheus 2.21.0 to 2.31.1. Prometheus 2.31.1 includes various features, enhancements, and fixes outlined in the Prometheus release notes.
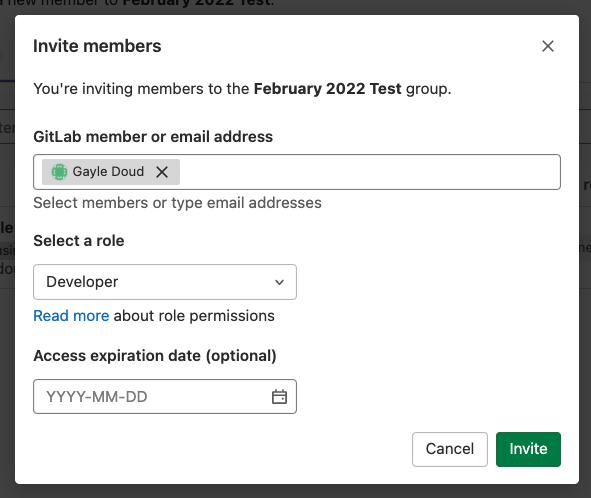
Invite members and groups by using a modal
Inviting members or groups to projects can now be completed through a modal experience. You no longer have to complete these steps in a form. The move to the modal interaction makes it easier for you to add members and groups to projects or groups from anywhere in the product, and minimizes disruption to your workflow.
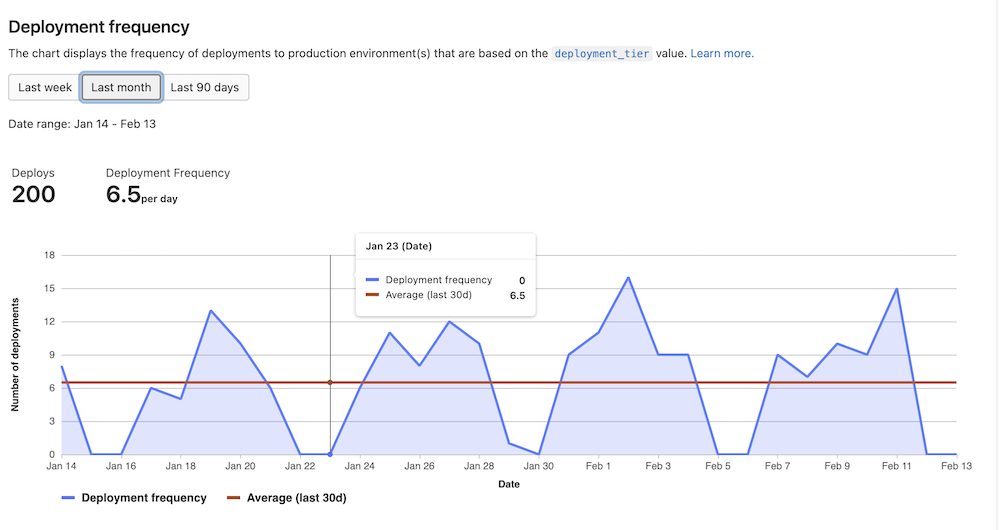
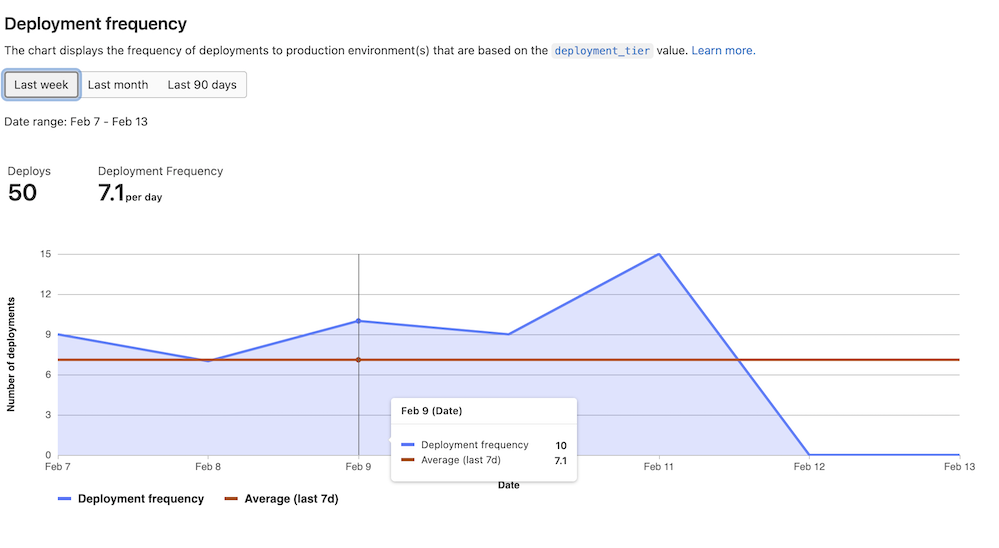
Additional data for deployment frequency graph
In this release, we’ve added the number of deployments and deployment frequency to DORA metrics displayed under CI/CD Analytics:
- Number of deployments shows the number of successful deployments in the date range
- Deployment frequency shows the average number of successful deployments.
This data previously appeared only in value stream analytics. With this additional information, you can gain a better understanding of your team’s deployment frequency for better tracking.
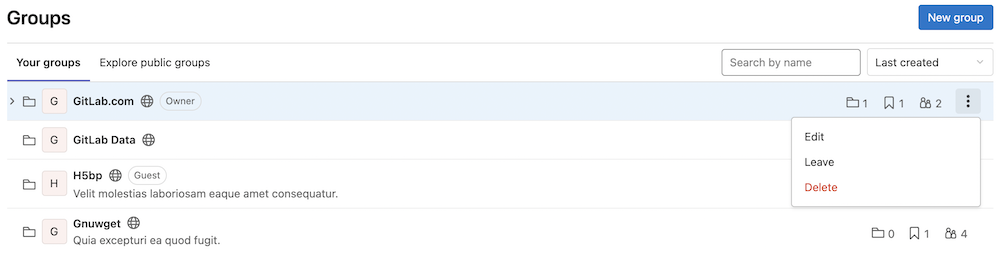
Delete groups at the parent group level
In this milestone, we’ve worked on one of the initial steps to reach feature parity between group owners (in any installation base) and administrator-only functionality that exists solely in the administrator panel for self-managed users.
Group owners can now delete a group and its subgroups from the parent group level. Until now, group owners had to go into each individual group to delete them, which was timely and inefficient. Group owners can now view all groups and delete them from a single place.
Add default issue and merge request templates in a project’s repository
In addition to defining default issue and merge request description templates in project settings, you can now set default templates in the .gitlab
directory of a project’s repository.
Do it by creating a Default.md file in the issue or merge request templates folders.
If default templates exist in both the project’s settings and in the repository, the template in the settings
takes precedence.
Thanks for the contribution @davebarr!
GitLab Runner 14.8
We’re also releasing GitLab Runner 14.8 today! GitLab Runner is the lightweight, highly-scalable agent that runs your build jobs and sends the results back to a GitLab instance. GitLab Runner works in conjunction with GitLab CI/CD, the open-source continuous integration service included with GitLab.
What’s new:
Bug Fixes:
The list of all changes is in the GitLab Runner CHANGELOG.
Use the CI Lint API with other branches or tags
Previously, the project CI lint API endpoint for validating CI/CD configuration was only capable of parsing configuration that exists in the default branch. In this release we’ve added an optional ref parameter to the endpoint, so you can now lint the CI/CD configuration you have in other branches or tag refs.
Deployment approval API
We are excited to introduce deployment approval via API. Prior to this feature, teams had the ability to protect an environment from any changes by requiring a manual job to be executed in a pipeline as a workaround. Now, deployment approval is a first-class concept in our platform. Teams can configure a number of approvers for a specific environment and use a new API endpoint to execute an approval or rejection of a deployment to that environment. This capability enables teams to create workflows to obtain the proper approvals before deploying software to production or other protected environments.
Latest Release badge for the project
We have added a new badge so you can easily see the version of your latest release right in the project page.
Thank you Jason D’Amour for your contribution!
Set custom rate limiting for GitLab Pages
We have added rate limiting capabilities to our Pages feature. Unlimited or undesired traffic (such as a Denial of Service attack) to hosted pages can cause unexpected availability issues or even downtime for users. With this update, rate limiting can be enforced per specific client IP addresses and per specific hosted pages domain. Limits can be configured for each independently. When enabled and traffic exceeds these limits, requests will be reported and rejected.
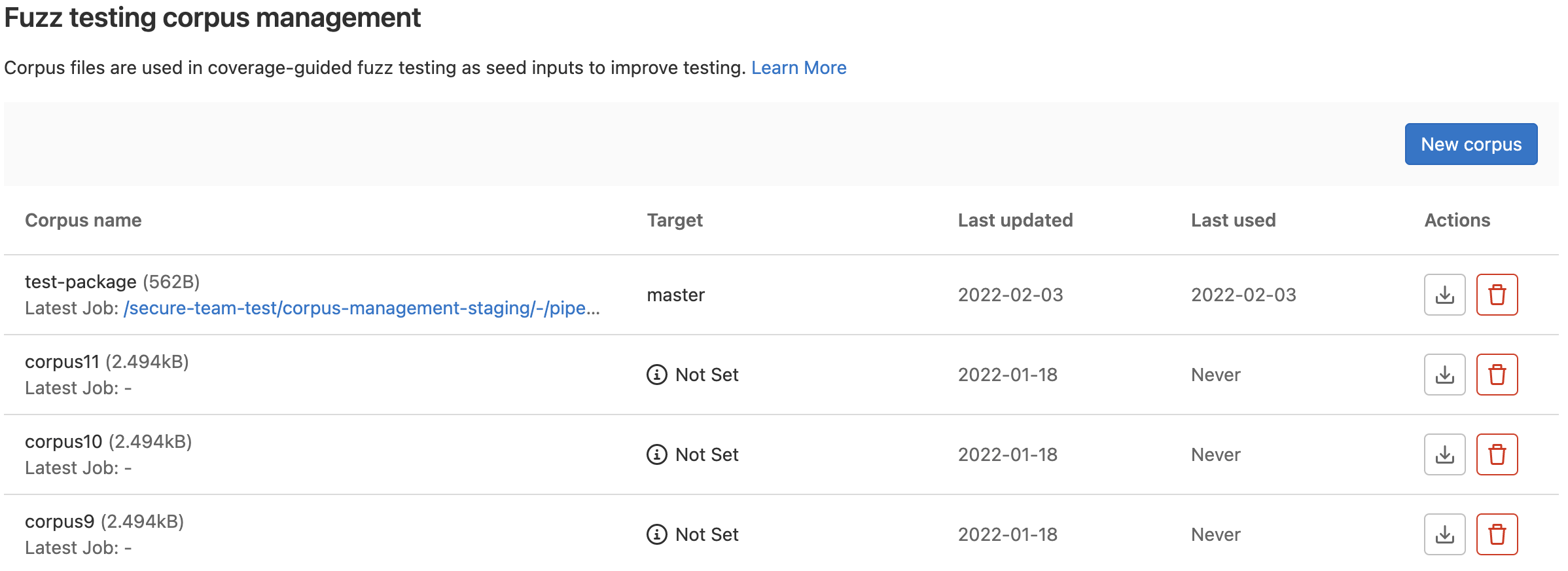
Coverage-guided fuzz testing corpus management
In previous versions of GitLab, if you wanted to use a seed corpus in a coverage-guided fuzz test, you would need to upload the file to a location and define the path to the corpus via the COVFUZZ_SEED_CORPUS variable. The management of any corpus that you might use in a test was completely manual, including updating the corpus after running a test. With GitLab 14.8, corpus management is now integrated into the Security & Compliance Configuration section. By setting the COVFUZZ_USE_REGISTRY to "true", setting the COVFUZZ_GITLAB_TOKEN variable to a personal access token, and specifying the corpus name via the COVFUZZ_CORPUS_NAME variable, corpus management can be easily integrated into your testing workflow. Corpus files can be automatically added to the registry from pipelines as coverage-guided fuzz tests are run. They can also be automatically updated with the artifacts output from a coverage-guided fuzz test job, rather than only manually updated. If a corpus is no longer needed, you can delete it directly from the registry page. Corpus files that are listed in the registry can also be downloaded for inspection or use elsewhere. This management UI provides a major improvement to the coverage-guided fuzz testing experience when seed corpuses are used.
Mutual TLS for DAST scans
Starting in GitLab 14.8, Mutual TLS is now available for DAST scans. This allows for a target application server to verify that requests are from a known source. Sites that utilize mutual TLS can now be scanned by DAST. To use mutual TLS, a masked variable named DAST_PKCS12_CERTIFICATE_BASE64 must be created and the base64-encoded PKCS12 certificate’s value must be stored in that variable. In addition, a masked variable name DAST_PKCS12_PASSWORD should be used to store the PKCS12 certificate’s password. Please note that this feature is not yet supported by the browser-based DAST scanner, which is still in beta.
SAST severities now available for .NET
Previously, GitLab SAST returned an Unknown severity for all vulnerabilities identified in .NET projects. Now, .NET results are assigned a severity value based on the CWE associated with the finding.
Severity levels are included in the gl-sast-report.json artifact in all GitLab tiers.
With GitLab Ultimate, these new severity levels make it easier to secure your .NET projects by requiring approval for merge requests and analyzing your overall risk posture.
For backwards compatibility reasons, severities will not appear in results by default until you upgrade to GitLab 15.0.
To receive .NET SAST results with severity values before then, update your .gitlab-ci.yml file to pin to the new major version, v3, of the Security Code Scan analyzer.
You can add this code snippet to your .gitlab-ci.yml file to try these new scanning capabilities.
In GitLab 15.0, we will promote this new version to run by default.
Filters added to Geo sites dashboard
The Geo sites dashboard allows administrators to view and edit details about their Geo primary and secondary sites. For customers operating multiple secondary sites, it can take time to scroll through the list of sites and identify the ones that need attention. We have added options to filter by health status, site name, or its URL. This makes it easier and faster to find what you are looking for on the dashboard.
Omnibus improvements
- GitLab 14.8 includes Mattermost 6.3, with Playbooks translations and streamlined notifications. Boards is promoted to Generally Available and includes change notifications, person avatars, and comment sort order. This version also includes security updates and upgrade from earlier versions is recommended.
- Securing Consul cluster in GitLab 14.8 is now easier. Users can now configure mTLS and Gossip encryption on Consul nodes to secure the communication between Consul agents and the clients.
- GitLab 14.8 also includes packages for SUSE Enterprise Linux Server (SLES) 15 SP2.















We want to hear from you
Enjoyed reading this blog post or have questions or feedback? Share your thoughts by creating a new topic in the GitLab community forum.
Share your feedback