API endpoint to get project transfer locations
We added a new Projects API endpoint that returns a list of groups to which you can transfer the specified project. Previously, you could select which group to transfer a project to from the dropdown list, which didn’t include groups made available through group sharing. Now, the new endpoint ensures that these groups are included too.
Import more relationships when importing projects from GitHub
Importing all supported relationships during a project import from GitHub can take a long time and is disabled by default.
Specifically:
Now you can include these additional relationships in an import if you require them, which slows down the import
but includes more information. To import additional relationships, go to the GitHub import page and select appropriate
checkboxes under Advanced import settings.
For more information on related features available in GitLab 15.5, see:
Modify user’s commit email through the Users API
Previously, a user’s commit email could be modified only in the UI. Now, administrators can use the Users API to modify the commit email and perform this as a bulk action.
Thank you Neil Drumm for your contribution!
Update group members’ SAML and SCIM extern_uid with API
Previously, if there were changes to group members’ SAML or SCIM identifier (also known as the NameID), the only way to update it was by having users unlink and manually re-link their GitLab and SSO accounts. Now, group owners can update the extern_uid field in GitLab for both SAML and SCIM identities to match the SSO identifier using a new endpoint in the groups API.
Filter issues by health status
Imagine you need a quick view of issues in the current milestone which are at risk. We’ve taken issue health status to the next level, and with this improvement, users can now filter issues that have a specific health status.
Show blocking epics in the roadmap
Since the release of linked epics in 15.0, you could show blocking relationships among epics. With this additional improvement, you can now view that blocking relationship from the roadmaps view.
Unsaved changes to wiki pages are preserved
Anything can happen when you’re writing long-form content in a web browser. An accidental click could close your tab, your browser could crash, or your computer could run out of battery. In many areas of GitLab, content you haven’t posted is saved locally to prevent data loss. You can see this in action when commenting on issues and merge requests. Now you can rest a little easier knowing unsaved changes to wiki pages are preserved in the same way.
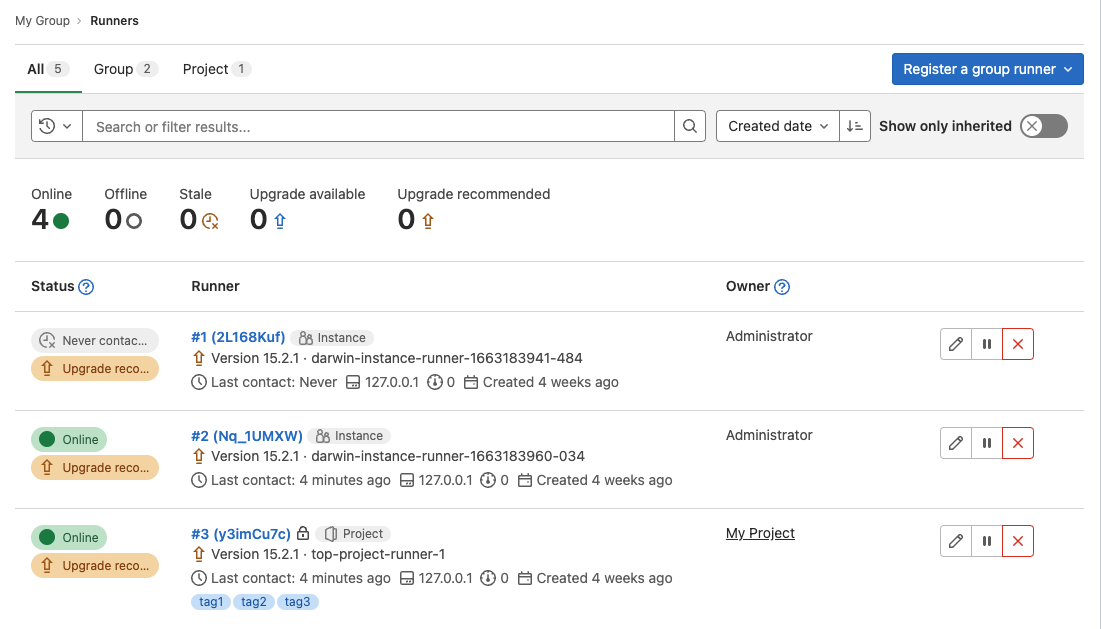
Display all available group runners
In the group runners list, you can now view all shared runners, runners from parent groups, and runners you administer. Previously, you could only view the runners you administer. This change provides a more comprehensive overview of group runners.
Expose CI/CD job token scope status in the jobs API endpoint
Since GitLab 14.4 you can limit the access scope of the CI/CD job token for a more secure CI_JOB_TOKEN workflow. If you wanted to determine if the setting was enabled in a project though, the only option was to manually go into the project’s settings. Starting in GitLab 15.5, you can check the response from the /jobs, /deployments and /environments API endpoints and programmatically verify the status of the setting.
Access release description from tag in CI/CD pipeline variable
In past releases, there was no easy way to configure a pipeline that refers to a release or to release notes associated with a tag. Now, you can refer to this information using two predefined environment variables: $CI_COMMIT_TAG_MESSAGE and $CI_RELEASE_DESCRIPTION.
FIPS compliant Kubernetes integration
The U.S. Government requires some GitLab customers to use FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standards) compliant software. You can now use the agent for Kubernetes on FIPS-enabled GitLab installations. This release also adds FIPS-compliant agent images that you can install on your clusters.
Prevent outdated deployment jobs
Previously, some outdated jobs could be manually started or retried even when Skip outdated deployment jobs is enabled. We have updated the logic for this setting to check the deployment status when a job starts. The job does not execute if the deployment job is outdated due to a more recent deployment. This check ensures that outdated deployment jobs are not accidentally started, overwriting more recent code changes in production.
Update a release using the Release CLI
In this milestone we added the ability to update a release using the Release CLI. You can use this to automate releases by updating any of the release attributes directly from the .gitlab-ci.yml file, and leveraging the CI/CD pipeline to do so.
Dependency scanning improved accuracy for Go dependencies
GitLab Dependency Scanning now uses a new method of detecting Go dependencies that is more accurate than the previous method and allows users to scan the correct version of the dependencies that are actually used by the application.
Static Analysis analyzer updates
GitLab Static Analysis includes many security analyzers that the GitLab Static Analysis team actively manages, maintains, and updates. The following analyzer updates were published during the 15.5 release milestone. These updates bring additional coverage, bug fixes, and improvements.
- Brakeman analyzer updated to fix a crash in False Positive Detection. See CHANGELOG for details.
- CodeClimate analyzer updated to version 0.87.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Kics analyzer updated to add additional rules, fix bugs, and update to kics version 1.6.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- NodeJSScan analyzer updated to fix an issue with error log processing. See CHANGELOG for details.
- PMD-Apex analyzer updated to version 6.49.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Secrets analyzer updated to Gitleaks version 8.12.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Security Code Scan analyzer updated to version 5.6.7. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Semgrep analyzer updated to version 0.115.0. See CHANGELOG for details.
- Update GitLab-managed rules to remove false positive results for:
- Java SQL injection
- C# LDAP injection
- C# XPath injection
- Fix a problem where Semgrep-based C# scanning created duplicate findings instead of combining them with Security Code Scan-based scan results.
- SpotBugs analyzer updated to version 4.7.2. See CHANGELOG for details.
If you include the GitLab-managed SAST template (SAST.gitlab-ci.yml), you don’t need to do anything to receive these updates. However, if you override or customize your own CI/CD template, you need to update your CI/CD configurations.
To remain on a specific version of any analyzer, you can pin to a minor version of an analyzer. Pinning to a previous version prevents you from receiving automatic analyzer updates and requires you to manually bump your analyzer version in your CI/CD template.
For previous changes, see last month’s updates.
Geo now replicates Incident Metric Images
With this release, Geo supports replication and verification of Incident Metric Images. This protects against loss of this data during failover if Geo is used as part of a disaster recovery strategy.
Improved code search quality for Advanced Search
This release improves code search quality for Advanced Search to bring it closer to the local IDE experience. You can now expect more relevant results for full tokens and some partial tokens as well as better matching for search terms with special characters.
If you created your index in GitLab 15.4 and earlier, you must update code search mappings. You can use zero-downtime reindexing or re-create your Advanced Search index from scratch.
Admin Area setting to prevent users from creating groups
GitLab administrators can now use the Admin Area to disable users’ permission to create top-level groups. Previously, administrators with access to the instance’s file system could change this setting only in the gitlab.rb file.
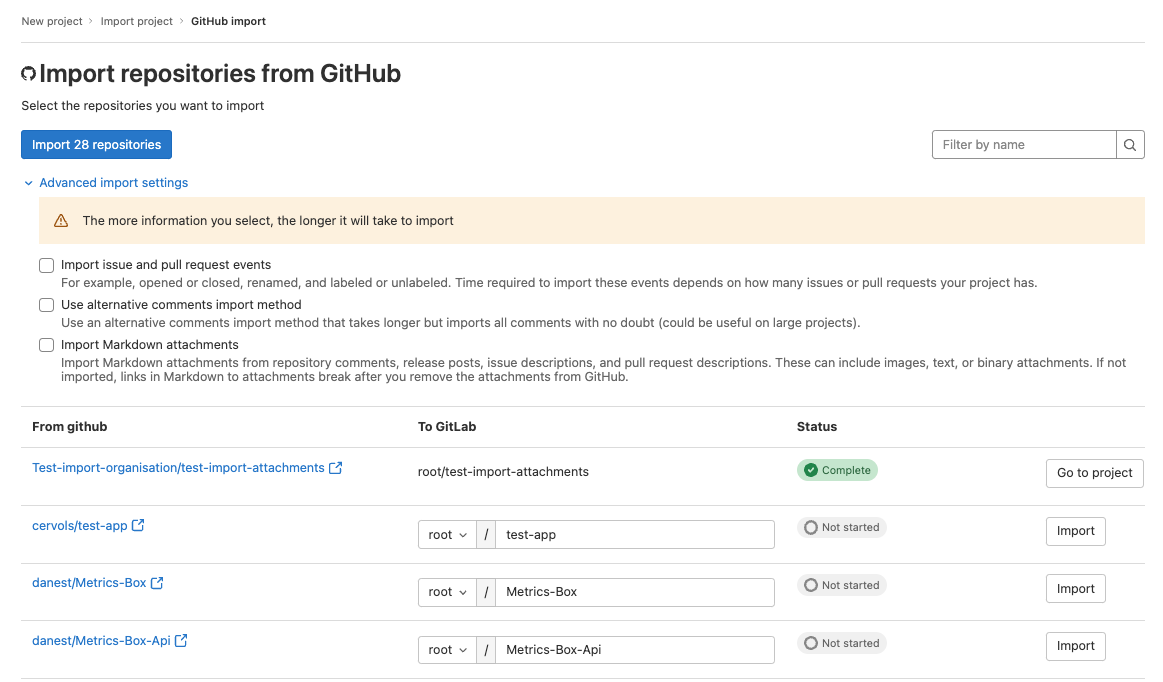
Import and store attachments when importing from GitHub
You can now import GitHub project image resources and other attachment types from release notes and comments.
The attachments are added to GitLab and their links are updated to new GitLab URLs.
Attachments aren’t imported by default because it can be a time intensive operation. To import them, go to the
GitHub import page, and select Import Markdown attachments under Advanced import settings when importing using
the GitLab UI.
For information on a related feature, see
Import more relationships when importing projects from GitHub.
Import pull request and issue events from GitHub
We continue to improve the GitHub project importer by adding more metadata to the migrated projects. With added
pull request events history, the following pull request events
can be imported from GitHub and become part of a merge request’s metadata:
- Closed or reopened.
- Labeled or unlabeled.
- Review requested or review request removed.
- Assigned or unassigned.
- Edited.
With added issue events history, the following issue events
can be imported from GitHub and become part of an issue’s metadata:
- Closed or reopened.
- Labeled or unlabeled.
- Milestone added or removed.
- Cross-referenced.
- Assigned or unassigned.
- Renamed.
Because importing pull request and issue events can take a long time, they aren’t imported by default. To import them,
go to the GitHub import page, and select Import issue and pull request events under Advanced import settings
when importing using the GitLab UI.
For information on a related feature, see
Import more relationships when importing projects from GitHub.
New filters for personal access token API
Prior to this release, API calls to retrieve personal access tokens (PATs) were relatively basic. Now, you can filter results on many properties and link filters together
to do complex filtering on parameters such as:
- When a token was last used.
- If a token is revoked.
- A token’s name.
These new API filters for PATs provide users and administrators more useful results from the PAT API.
Thank you Andreas Deicha for your contribution!
Add labels and dates to a task
You can now add dates and labels to a task to better reflect additional context related to the task. You can filter tasks by their labels or sort tasks by due date in a project, group, or dashboard issue list.
Improve DevOps efficiency with the pre-defined DORA comparison report
Following the recent release of the new DORA Insights custom reporting, we have added a pre-defined report to the default insights configuration file. The new report visualizes the performance of the four DORA metrics over the past 180 days, aggregated by month and day.
This report helps you learn the DORA framework, understand how to use the metrics, and see how they perform over time on real data.
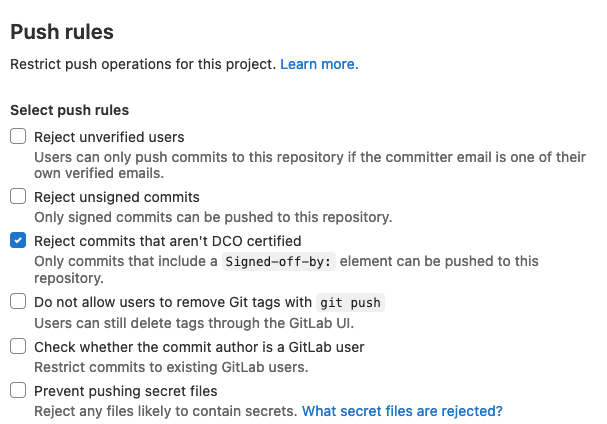
Enforce Developer Certificate of Origin on all contributions
The Developer Certificate of Origin (DCO) is a per-commit sign-off made by a contributor stating that they have the right to submit the code to the project. By signing off on a commit, the contributor agrees to the terms published at developercertificate.org.
Now, you can easily enforce this Developer Certificate via a per-project setting to prevent contributors from contributing code that violates your license. When enabled, all new commits must include such a certificate of origin in the form of a line in the commit message Signed-off-by:.
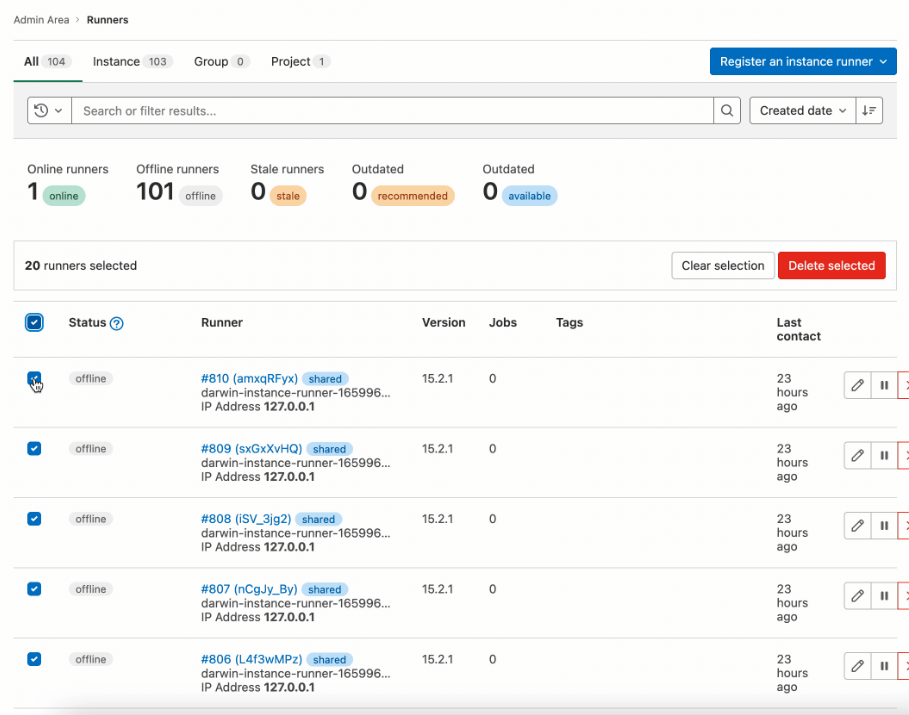
Bulk delete runners in the Admin Area
Bulk editing is a powerful and valuable feature when you need to visualize or manage large data sets. For administrators that manage a fleet of runners, the lack of a bulk delete option is a productivity drain and increases the operational overhead of maintaining runners. Now, in the Admin Area, you can select multiple runners and delete them at the same time. You can also select and delete a full page of runners at once.
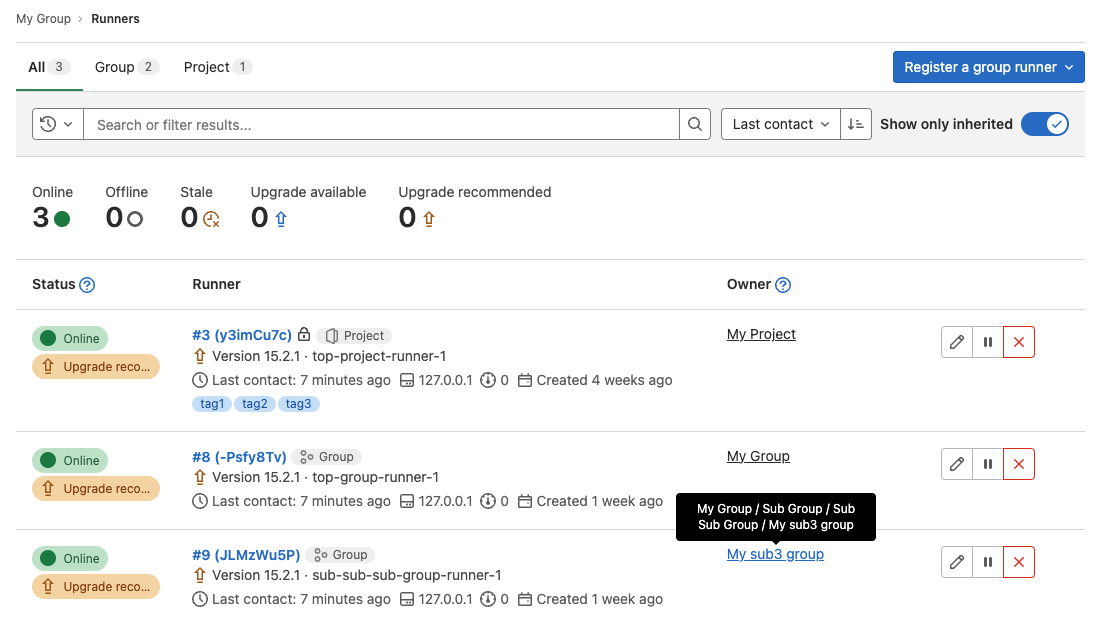
Display runner owner in Admin Area and group runners page
For GitLab administrators or group owners, locating a specific runner’s owner can be very time-consuming in environments where many runners are in use at the group or project level. This problem is even more acute and impactful to the customer if the runner in question is not picking up jobs or critical production jobs are running slowly. The Admin Area and group runners page now include an owner column so you can quickly determine the owner of any runner in the environment at a glance.
GitLab Runner 15.5
We’re also releasing GitLab Runner 15.5 today! GitLab Runner is the lightweight, highly-scalable agent that runs your CI/CD jobs and sends the results back to a GitLab instance. GitLab Runner works in conjunction with GitLab CI/CD, the open-source continuous integration service included with GitLab.
What’s new:
Bug Fixes:
The list of all changes is in the GitLab Runner CHANGELOG.
Create annotated tags in the Releases page
You can now create annotated tags and add them to your releases in the Releases page. You can use annotated tags to provide downstream users and applications with additional information about a release.
More kubectl calls for the agent CI/CD workflow
If you use the GitLab agent for Kubernetes with GitLab CI/CD on GitLab SaaS, previously you couldn’t use kubectl exec, attach, or cp calls. GitLab now supports these calls on top of the SPDY protocol. You can now use kubectl exec, attach, or cp in your CI jobs.
Unfortunately, some cloud providers do not support SPDY. GitLab is working with the Kubernetes community to ship Websockets support in Kubernetes, which will be the solution for many cloud-hosted GitLab instances.
Restrict the agent for Kubernetes by environment deployment tiers
Kubernetes administrators can now restrict CI/CD access to specific environment tiers with RBAC, using the agent for Kubernetes.
In past releases, administrators could not restrict access to specific tiers, which added potential security
risks to Kubernetes integrations.
Change the internal port for DAST API and API Fuzzing scans
In previous versions of GitLab, DAST API and API Fuzzing scans used a fixed internal port for communications between backend components. In some user configurations this caused a conflict with another configured service. In GitLab 15.5, you can use the DAST_API_API_PORT and FUZZAPI_API_PORT variables to configure the internal port number used by the scanners when it conflicts.
Run security scanning tools in merge request pipelines
GitLab application security scans run in CI/CD pipelines.
By default, scan jobs only run in branch pipelines.
Now, you can also run scans in merge request (MR) pipelines by switching to the Latest version of the CI/CD templates instead of the Stable version.
This makes it easier to use security scanning if you design your CI/CD pipelines around MR events.
We plan to update the Stable templates with this change in GitLab 16.0.
Note that Latest templates can receive breaking changes in any release.
To learn more about Stable and Latest templates, see documentation on CI/CD template versioning.
Use Code Quality with a private, authenticated image registry
The Code Quality scanner downloads and runs container images to scan your code.
Previously, you could pull these images from a custom image registry, but you couldn’t use a private registry that required authentication.
Now, you can provide a registry username and password by setting CI/CD variables when you include the Code Quality CI/CD template.
Geo now replicates alert metric images
If used as part of a disaster recovery strategy, Geo now supports replication and verification of alert metric images to protect against data loss.
GitLab chart improvements
- In the 15.4 release post, we announced that the GitLab Logger will be used by default for the GitLab Helm Chart in 15.5. This implementation has been delayed to 15.6. For users who have custom log parsers in place, be aware that this will automatically wrap all logs from plaintext to structured JSON.
- Cloud Native GitLab will replace
alpine-certificates behaviors with gitlab-base. To prevent differential behaviors between Alpine and Debian, and increase consistency across containers, we are going to build the pattern on gitlab-base. This means operational service containers will share a common root layer, which provides an efficiency boost to Pod instantiation time. The user impact of this, is that we will be changing the image name and tags used. We will maintain a mirrored tag for a brief period.
- The GitLab Helm Chart will have a new major version release before the next major GitLab version, separate from the next major version as a whole. We are not sure when this next Helm chart major version will be released, but it can be expected no sooner than 3 milestones, but it may be longer. This major Helm chart release will require downtime, as we incorporate large updates and require manual intervention for upgrade paths.









We want to hear from you
Enjoyed reading this blog post or have questions or feedback? Share your thoughts by creating a new topic in the GitLab community forum.
Share your feedback