Configurable import jobs limit
Until now, the maximum number of import jobs for:
- GitHub importer was 1000.
- Bitbucket Cloud and Bitbucket Server importers was 100.
These limits were hard-coded and couldn’t be changed. These limits might have slowed down imports, because they might have been insufficient
to allow the import jobs to be processed at the same rate they were enqueued.
In this release, we’ve moved the hard-coded limits to application settings. Although we are not increasing these limits on GitLab.com, administrators
of self-managed GitLab instances can now configure the number of import jobs according to their needs.
GitLab for Slack app configurable for groups and instances
Previously, you could configure the GitLab for Slack app for one project at a time only. With this release, it’s now possible to configure the integration for groups or instances and make changes to many projects at once.
This improvement brings the GitLab for Slack app closer to feature parity with the deprecated Slack notifications integration.
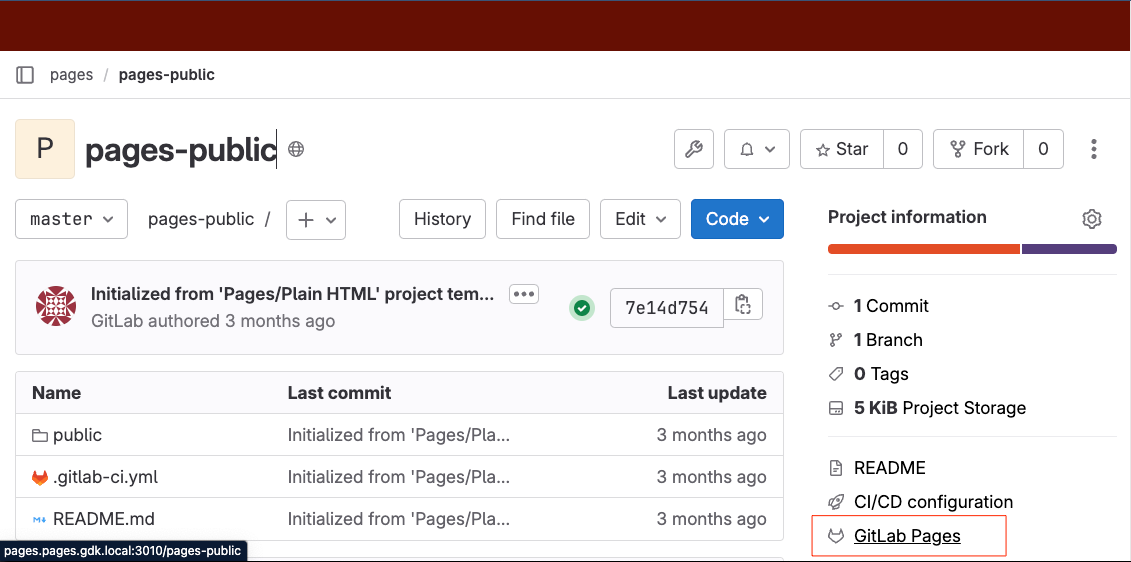
Improved GitLab Pages visibility in sidebar
In previous releases, for projects with a GitLab Pages site, it was difficult to find the site URL.
From GitLab 16.11, the right sidebar has a shortcut link to the site, so you can find the URL without needing to check the docs.
Visually distinguish epics using colors
To further improve the ability to use portfolio management features across the organization, you can now distinguish epics using colors on roadmaps and epic boards.
Quickly distinguish between group ownership, stage in a lifecycle, development towards maturity, or a number of other categorizations with this lightweight but versatile feature.
Automate the creation of Google Compute Engine Runners from GitLab - Public Beta
Previously, creating GitLab Runners in Google Compute Engine required multiple context switches from GitLab and Google Cloud.
Now, you can easily provision GitLab Runners in Google Compute Engine with a terraform template from the GitLab Runner Infrastructure Toolkit and GitLab to deploy a GitLab runner and provision the Google Cloud infrastructure - without having to switch between multiple systems.
Expanded Hashicorp Vault Secrets support, including Artifactory and AWS
The GitLab integration with HashiCorp Vault has been expanded to support more types of secrets. You can now select a generic type of secrets engine, introduced in GitLab Runner 16.11. This generic engine supports HashiCorp Vault Artifactory Secrets Plugin and AWS secrets engine. Use this option to safely retrieve the secrets you need and use them in GitLab CI/CD pipelines!
Thanks so much to Ivo Ivanov for this great contribution!
Improve automatic retry for failed CI jobs with specific exit codes
Previously, you could use retry:when in addition to retry:max to configure how many times a job is retried
when specific failures occur, like when a script fails.
With this release, you can now use retry:exit_codes
to configure automatic retries of failed jobs based on specific script exit codes.
You can use retry:exit_codes with retry:when and retry:max to fine-tune your pipeline’s behavior
according to your specific needs and improve your pipeline execution.
Thanks to Baptiste Lalanne for this community contribution!
Connect Google Artifact Registry to your GitLab project
You use the GitLab container registry to view, push, and pull Docker and OCI images alongside your source code and pipelines. For many GitLab customers, this works great for container images during the test and build phases. But, it’s common for organizations to publish their production images to a cloud provider, like Google.
Previously, to push images from GitLab to Google Artifact Registry, you had to create and maintain custom scripts to connect and deploy to Artifact Registry. This was inefficient and error prone. In addition, there was no way easy way to get a holistic view of all of your container images.
Now, you can leverage the new Google Artifact Management feature to easily connect your GitLab project to an Artifact Registry repository. Then you can use GitLab CI/CD pipelines to publish images to the Artifact Registry. You can also view images that have published to the Artifact Registry in GitLab by going to Deploy > Google Artifact Registry. To view details about an image, simply select an image.
This feature is in Beta and is currently available only on GitLab.com.
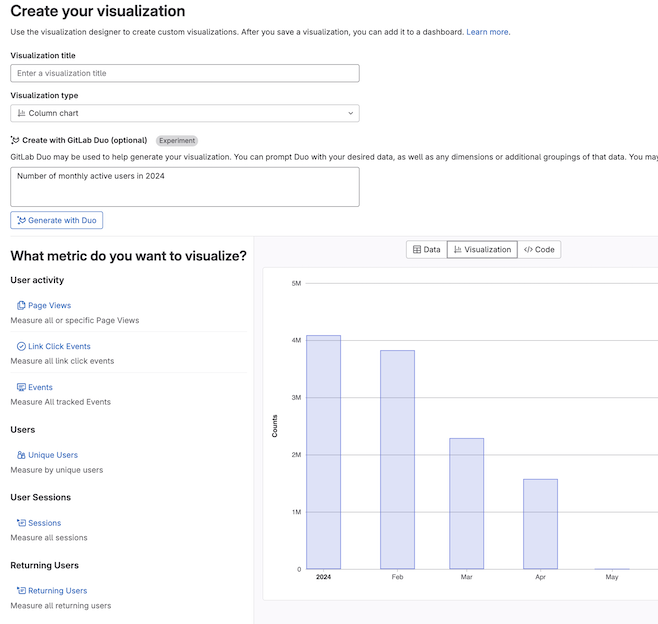
Explore your Product Analytics data with GitLab Duo
Product Analytics is now generally available, and this release includes a custom visualization designer. You can use it to explore your application event data, and build dashboards to help you understand your customers’ usage and adoption patterns.
In the visualization designer, you can now ask GitLab Duo to build visualizations for you by entering plain text requests, for example “Show me the count of monthly active users in 2024” or “List the top urls this week.
GitLab Duo in Product Analytics is available as an Experimental feature.
You can help us mature this feature by providing feedback about your experience with GitLab Duo in the custom visualization designer in this feedback issue.
Dependency Scanning support for Yarn v4
Dependency Scanning supports Yarn v4. This enhancement allows our analyzer to parse Yarn v4 lockfiles.
Authenticate to Google Cloud with workload identity federation
Workload identity federation allows you to securely connect workloads between GitLab and Google Cloud without the use of service account keys. This improves security, because keys can potentially be long-lived credentials that expose a vector for attack. Keys also come with management overhead for creating, securing, and rotating.
Workload identity federation allows you to map IAM roles between GitLab and Google Cloud.
This feature is in Beta and is currently available only on GitLab.com.
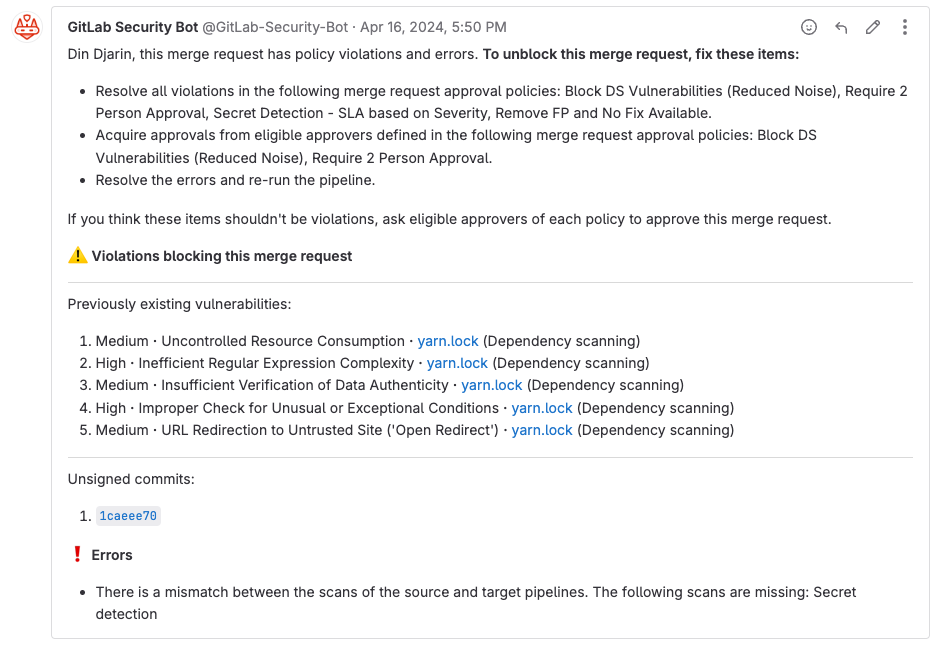
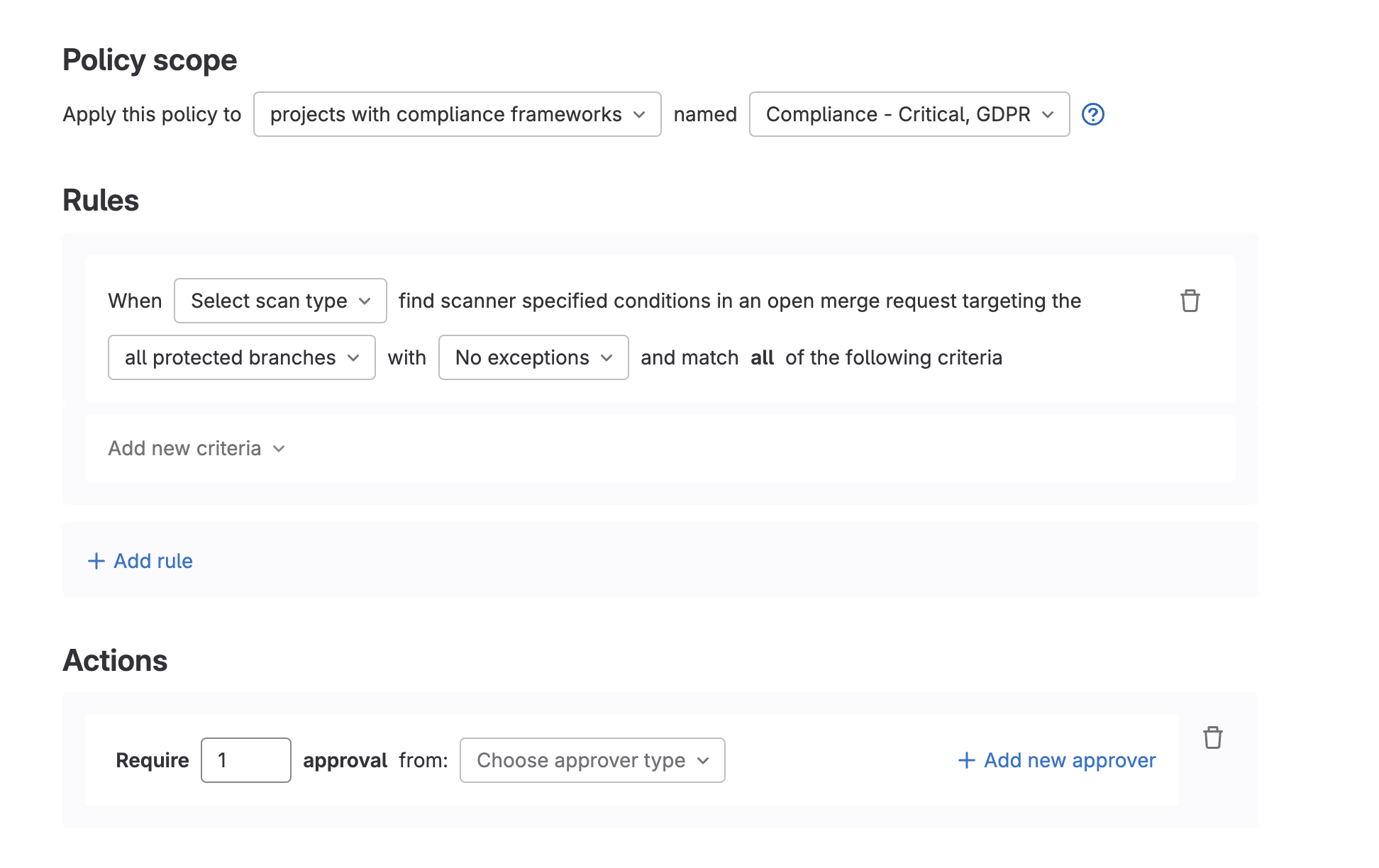
Extend policy bot comment with violation data
The security policy bot gives users context to understand when policies are enforced on their project, when evaluation is completed, and if there are any violations blocking an MR, with guidance to resolve them. We have now extended support in the bot comment to supply additional insight into why an MR may be blocked by a policy, with more granular feedback on how to resolve. Details provided by the comment include:
- Security findings that are specifically blocking the MR
- Out-of-policy licenses
- Policy errors that may default in a “fail closed” and blocking behavior
- Details regarding the pipelines that are being considered in the evaluation for security findings
With these extra details, you can now more quickly understand the state of your MR and self-serve to troubleshoot any issues.
More username options
Usernames can only include non-accented letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
Usernames must not start with a hyphen (-), or end in a period (.), .git, or .atom.
Username validation now more accurately states this criteria. This improved validation means that you are clearer on your options when choosing your username.
Thank you Justin Zeng for your contribution!
Users list search and filter improvements
The Admin Area users page has been improved.
Previously, tabs horizontally spanned across the top of the users list, making it difficult to navigate to the desired filter.
Now, filters have been combined into the search box, making it much easier to search and filter users.
Thank you Ivan Shtyrliaiev for your contribution!
Omnibus improvements
-
In GitLab 17.0, the minimum-supported version of PostgreSQL will become 14. In preparation for this change, in GitLab 16.11 we have changed the
attempt_auto_pg_upgrade? setting to true, which will attempt to automatically upgrade the version of PostgreSQL to 14.
This process is the same as for last time we bumped the minimum-supported PostgreSQL version.
Custom webhook headers
Previously, GitLab webhooks did not support custom headers. This meant you could not use them with systems that accept authentication tokens from headers with specific names.
With this release, you can add up to 20 custom headers when you create or edit a webhook. You can use these custom headers for authentication to external services.
With this feature and the custom webhook template introduced in GitLab 16.10, you can now fully design custom webhooks. You can configure your webhooks to:
- Post custom payloads.
- Add any required authentication headers.
Like secret tokens and URL variables, custom headers are reset when the target URL changes.
Thanks to Niklas for this community contribution!
Test project hooks with the REST API
Previously, you could test project hooks in the GitLab UI only. With this release, you can now trigger test hooks for specified projects by using the REST API.
Thanks to Phawin for this community contribution!
Value stream events can now be calculated cumulatively
We introduced a more robust method for calculating durations between label events. This change accommodates scenarios where events occur multiple times, such as label changes in merge requests back and forth between development to review states. Previously, the duration was calculated as the total time elapsed between the first and last label event.
Now, the duration is calculated as cumulative time, meaning it now correctly represents only the time when an issue or merge request had a given label.
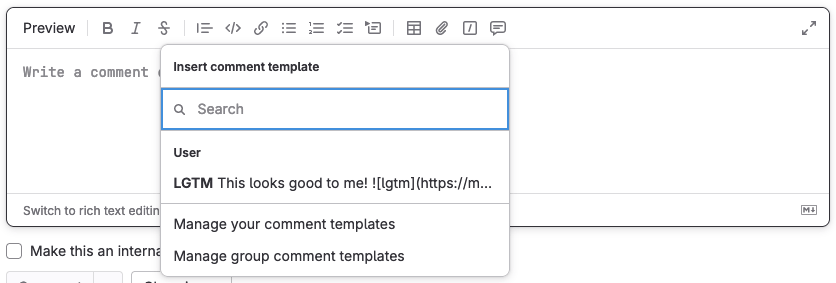
Group comment templates
Across an organization it can be helpful to have the same templated response in issues, epics, or merge requests. These responses might include standard questions that need to be answered, responses to common problems, or maybe structure for merge request review comments.
Group comment templates enable you to create saved responses that you can apply in comment boxes around GitLab to speed up your workflow. This new addition to comment templates allows organizations to create and manage templates centrally, so all of their users benefit from the same templates.
To create a comment template, go to any comment box on GitLab and select Insert comment template > Manage group comment templates. After you create a comment template, it’s available for all group members. Select the Insert comment template icon while making a comment, and your saved response will be applied.
We’re really excited about this next iteration of comment templates and will also be adding project-level comment templates soon too. If you have any feedback, please leave it in issue 45120.
Control who can download job artifacts
By default, all generated artifacts from CI/CD jobs in a public pipeline are available for download by all users with access to the pipeline. However, there are cases where artifacts should never be downloaded, or only be accessible for download by team members with a higher access level.
So in this release, we’ve added the artifacts:access keyword. Now, users can control whether artifacts can be downloaded by all users with access to the pipeline, only users with the Developer role or higher, or no user at all.
GitLab Runner 16.11
We’re also releasing GitLab Runner 16.11 today! GitLab Runner is the lightweight, highly-scalable agent that runs your CI/CD jobs and sends the results back to a GitLab instance. GitLab Runner works in conjunction with GitLab CI/CD, the open-source continuous integration service included with GitLab.
Bug Fixes:
The list of all changes is in the GitLab Runner CHANGELOG.
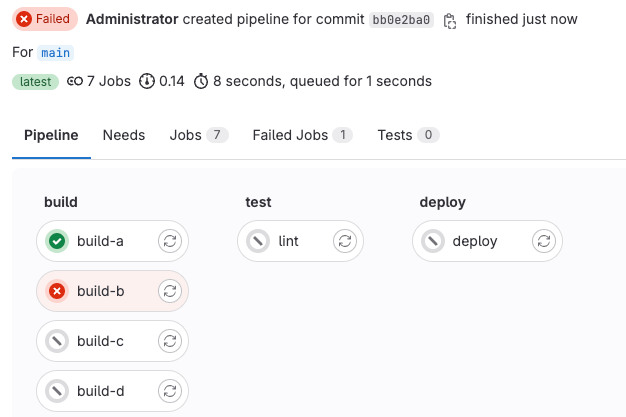
Improved pipeline details page
The pipeline graph offers a comprehensive overview of your pipelines, showing job statuses, runtime updates, multi-project pipelines, and parent-child pipelines.
Today, we’re excited to announce the release of the redesigned pipeline graph with enhanced aesthetics, grouped jobs visualization, improved mobile expirence and expanded downstream pipeline visibility within your existing view.
We’d greatly appreciate it if you could try it out and share your feedback through this dedicated issue.
Build step of Auto DevOps upgraded
Because the heroku/buildpacks:20 image used by the Auto Build component of Auto DevOps was deprecated upstream, we are moving to the heroku/builder:20 image.
This breaking change arrives outside a GitLab major release to accommodate a breaking change upstream. The upgrade is unlikely to break your pipelines. As a temporary workaround, you can also manually configure the heroku/builder:20 image and skip the builder sunset errors.
Additionally, we’re planning another major upgrade from heroku/builder:20 to heroku/builder:22 in GitLab 17.0.
DAST analyzer performance updates
During the 16.11 release milestone we completed the following DAST improvements:
- Snip navigation paths to improve crawler performance, which reduced scan time by 20% according to our benchmark test. See the issue for more details.
- Optimize DAST reporting to reduce memory usage, which reduced runner memory spikes during DAST scans. See the issue for more details.
Dependency graph support for dependency scanning SBOMs
Users can access dependency graph information in CycloneDX SBOMs generated as a part of their dependency scanning report. Dependency graph information is available for the following package managers:
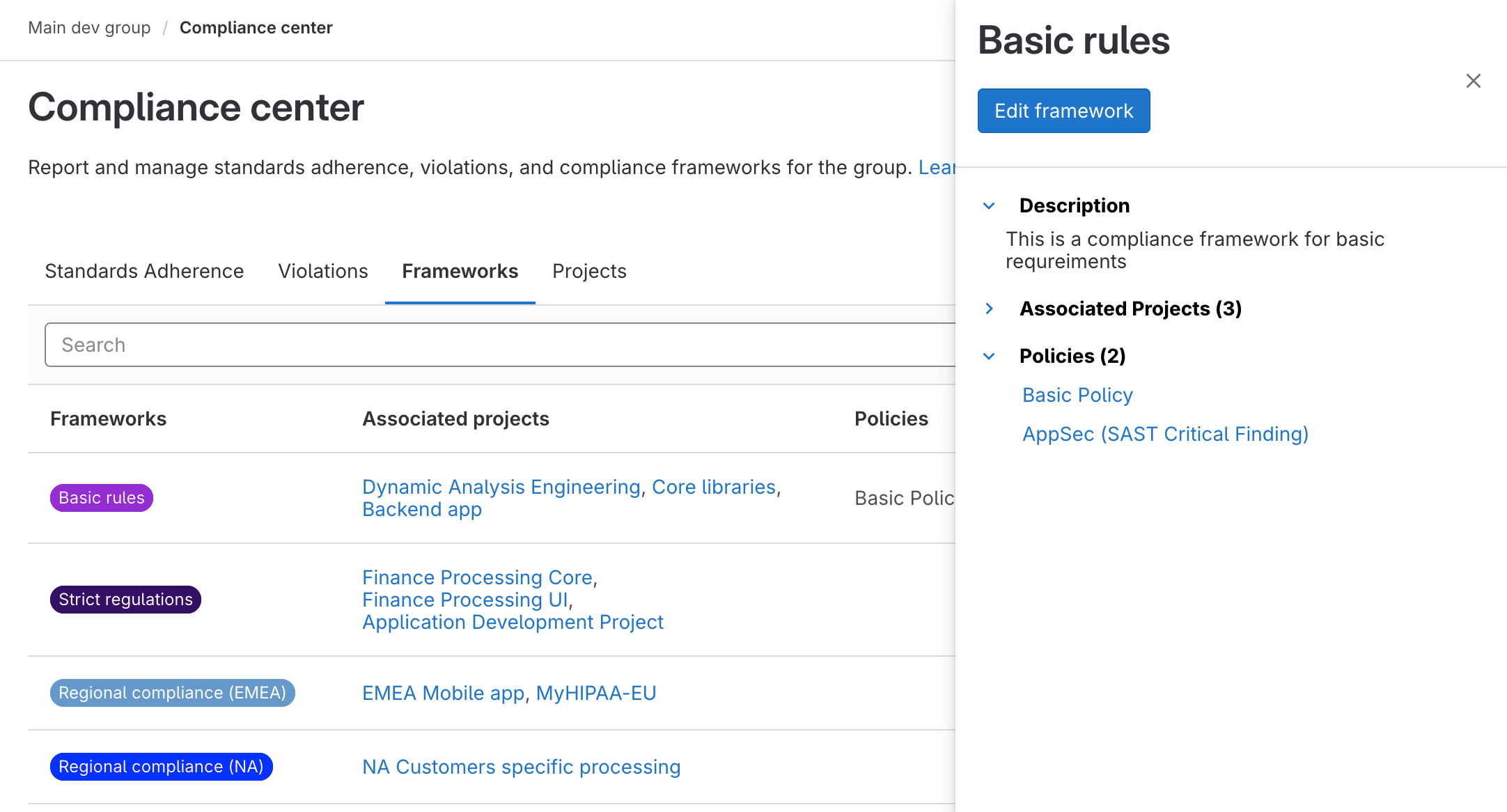
Display linked Security Policies in Compliance Frameworks
As the compliance center becomes the battle station for compliance managers, you can now manage compliance frameworks, and also gain insight into controls that have
been created through security policies and linked to a compliance framework.
Enforce security scanners to run in projects that are in-scope for your compliance, enforce two-person approval, or enable vulnerability management workflows
through these extensive controls and then roll them up to a compliance framework, ensuring relevant projects within the framework are properly enforced by the control.
Issue with duplicate security policies resolved
In GitLab 16.9 and earlier, it was possible for a project to both inherit security policies from a parent group or subgroup and link to the same security policies project. The result was that policies were duplicated in the policies list.
This issue has been resolved and it is no longer possible to link to a security policies project from which policies are already inherited.
Renew application secret with API
You can now use the Applications API to renew application secrets. Previously, you had to use the UI to do this. Now you can use the API to rotate secrets programatically.
Thank you Phawin for your contribution!
Webhook notifications for expiring group and project access tokens
Webhook events for project and group access tokens are now available.
Previously, email was the only way to get notifications about expiring tokens. A webhook event, if triggered, will be triggered seven days before an access token expires.
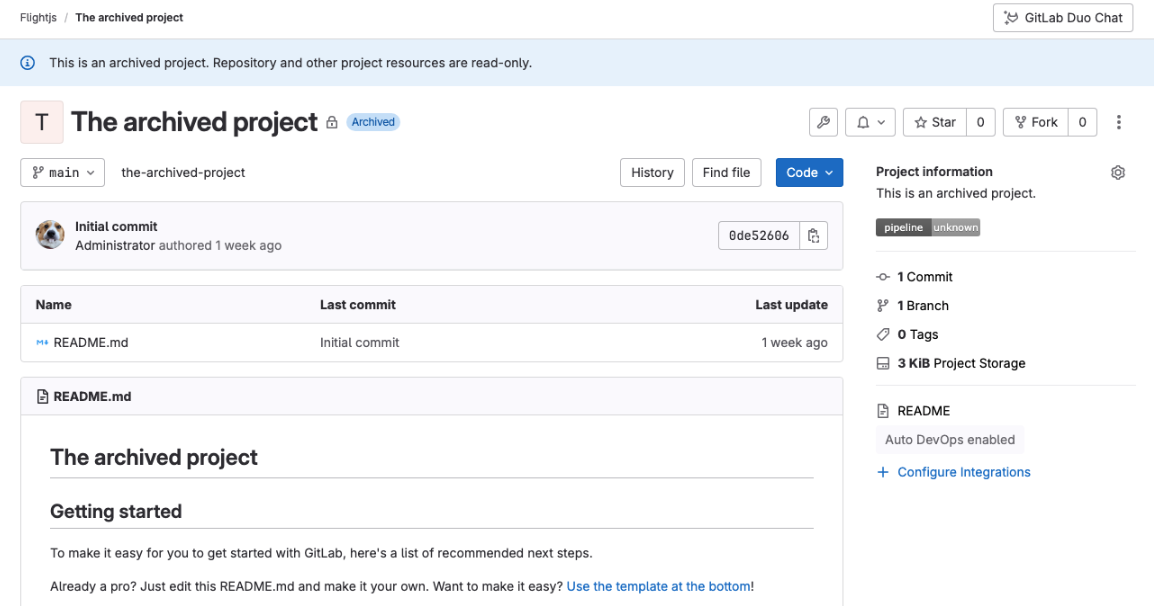
Updated project archiving functionality
Now it’s easier to identify archived projects in project lists. From 16.11, archived projects display an Archived badge in the Archived tab of the group overview. This badge is also part of the project title on the project overview page.
An alert message clarifies that archived projects are read-only. This message is visible on all project pages to ensure that this context is not lost even when working on sub-pages of the archived project.
In addition, when deleting a group, the confirmation modal now lists the number of archived projects to prevent accidental deletions.








We want to hear from you
Enjoyed reading this blog post or have questions or feedback? Share your thoughts by creating a new topic in the GitLab community forum.
Share your feedback